Kindy Uplift funding is provided to respond to children's learning and development needs through evidence-based initiatives that lift outcomes for kindergarten children.
Kindy Uplift can be used to fund professional development, programs, resources and supports to build teacher and educator capability and support inclusion in all approved kindergarten programs, including sessional and long day care kindergarten services.
Kindy Uplift priority areas
Kindy Uplift funding will be used to strengthen children's access to, and meaningful participation in, the full range of kindergarten experiences.
Services will demonstrate how Kindy Uplift funding is used to improve outcomes for kindergarten children, through data-informed planning.
Kindy Uplift focuses on 6 priority areas that align with the Early Years Learning Framework (EYLF) V2.0 and learning outcomes.
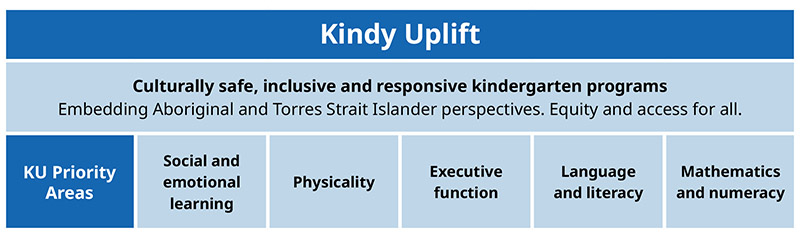
-
Culturally safe, inclusive and responsive kindergarten programs
-
Embedding Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander perspectives—creating culturally safe places, working in intercultural ways through pedagogy and practice, engaging with Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples and embedding perspectives in planning and implementation of curriculum.
-
Equity and Access for all—recognising and responding to the needs of children more likely to experience educational disadvantage within the service and community. This includes consideration to family diversity, cultural and linguistic differences and any barriers to meaningful engagement and participation.
-
Social and emotional learning—social learning involves the development of children's communication skills, social skills, social regulation skills and awareness of others. Emotional learning is focused on identifying and regulating emotions and understanding the emotions of others.
-
Physicality—the skills and abilities that support children to learn to move with stability, control and awareness of their environment and to manage the control of objects. Physicality includes gross motor development, fine motor development and integrates consideration of sensory learning.
-
Executive function—a set of cognitive skills that enable children to sustain focus, control impulses, and achieve goals. These skills are important for learning and include working memory, inhibitory control and cognitive flexibility, observable through behaviours such as persistence, adaptability and problem solving.
-
Language and literacy—how children use words, gestures, sounds and symbols in order to express their thoughts and communicate effectively, both receptively and expressively.
-
Mathematics and numeracy—the development of understandings about numbers, quantity, concepts of time, length, distance, capacity and area in everyday play.